See The Northern Lights Tonight: Aurora Forecast
Ever wondered what paints the night sky with ethereal, dancing lights? The aurora borealis and australis, nature's grand light shows, are a testament to the dynamic interplay between the Sun and Earth. These mesmerizing displays aren't mere random occurrences; they're governed by complex solar and terrestrial phenomena, intricately tied to the auroral oval.
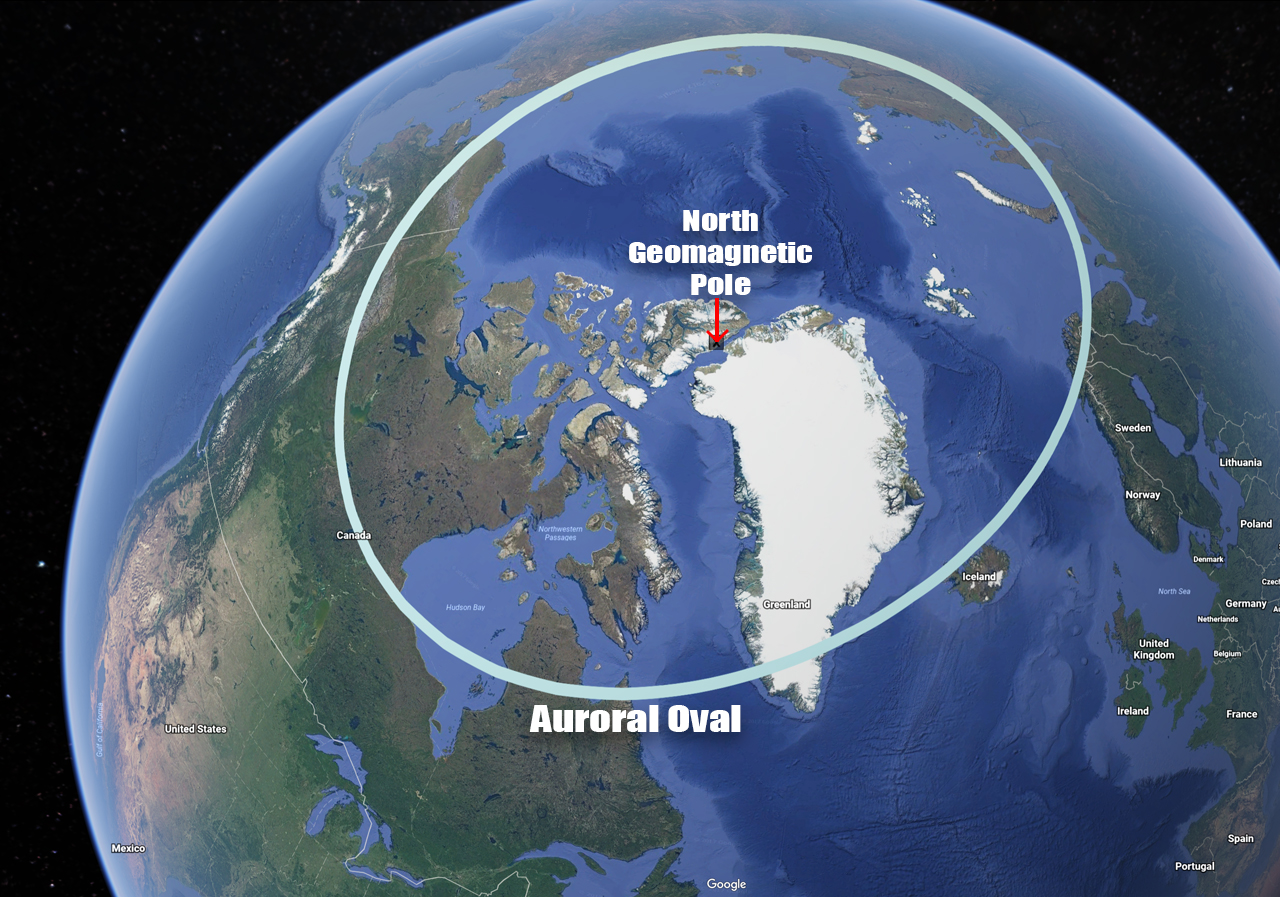
The auroral oval, a constantly shifting ring encircling Earth's magnetic poles, marks the region where these captivating lights are most likely to appear. Imagine a luminous halo, sometimes a vibrant green, other times a fiery red, draped around the polar regions. Its location and intensity fluctuate, responding to the solar wind's capricious temperament. When solar activity is high, the oval expands, bringing the aurora to lower latitudes. Conversely, during periods of solar quiescence, it contracts, clinging closer to the poles. This dynamic behavior is driven by the interaction between charged particles from the Sun and Earth's magnetic field.
| Phenomenon | Auroral Oval |
| Description | A ring-shaped region around Earth's magnetic poles where auroras are most frequently observed. |
| Cause | Interaction of solar wind (charged particles from the Sun) with Earth's magnetosphere and atmosphere. |
| Appearance | Typically appears as a band of light, ranging in color from green to red, and can exhibit various shapes and dynamic movements. |
| Visibility | Most visible at high latitudes, but can extend to lower latitudes during periods of increased solar activity. |
| Predictability | Scientists use various models and real-time data to predict auroral activity, but it remains a complex and dynamic phenomenon. |
| Further Information | NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center |
Predicting the aurora's appearance is a challenging but increasingly accurate scientific endeavor. Researchers utilize real-time solar wind data, monitoring the Kp index (a measure of geomagnetic activity), the interplanetary magnetic field (Bz), and other key indicators. Sophisticated models, like the OVATION Aurora Forecast Model, provide valuable insights, helping aurora enthusiasts pinpoint optimal viewing locations and times.
The colors of the aurora are a direct result of the interaction between solar particles and atmospheric gases. Oxygen, the most abundant gas in our atmosphere, produces the characteristic green and red hues. High-altitude oxygen molecules, energized by colliding solar particles, emit a vivid green light. At lower altitudes, these collisions can generate a red glow. Nitrogen, another atmospheric component, contributes to the auroral palette with blue and violet tints.
Imagine standing beneath a sky ablaze with shimmering curtains of light, a breathtaking spectacle of color and movement. The aurora is more than just a visual treat; it's a powerful reminder of our planet's place in the vast cosmic ballet. It underscores the constant interaction between Earth and the Sun, a relationship that both sustains life and generates these awe-inspiring displays.
Understanding the auroral oval is key to unlocking the secrets of these celestial displays. From its shape and location to its color and intensity, the oval provides a window into the intricate dynamics of space weather. By tracking this elusive ring of light, we can better appreciate the magnificent natural phenomenon that is the aurora borealis and australis. Spaceweatherlive.com offers a wealth of near real-time information on space weather and auroral activity, providing a valuable resource for those eager to witness the aurora's enchanting dance.
The journey to witnessing the Northern Lights often begins with the question, "Is there any aurora now?" Resources like real-time aurora detectors and geomagnetic perturbation maps offer answers, guiding observers toward the best viewing opportunities. Elias Loomis's 1860 map, depicting the auroral oval's average position, was a pioneering step in understanding auroral geography. Today, sophisticated models and data visualization tools allow for far more precise and dynamic predictions.
The scientific community continuously refines its understanding of the aurora. From analyzing historical data to leveraging cutting-edge technology like the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), researchers delve into the complexities of auroral activity and its impact on our planet. The ionosphere, a region of the atmosphere significantly influenced by auroral activity, plays a crucial role in radio communication and navigation. Studying the ionosphere's response to geomagnetic storms is essential for ensuring the reliability of these critical systems.
The aurora, a captivating display of light and color, is a testament to the dynamic and interconnected nature of our solar system. From the Sun's energetic outbursts to the Earth's protective magnetic field, the aurora is a visible manifestation of the forces at play in the cosmos. Whether you're a seasoned aurora chaser or simply captivated by the beauty of the night sky, understanding the science behind the auroral oval enriches the experience of witnessing this extraordinary phenomenon.