Securely Managing IoT Devices Behind A Firewall
How can businesses ensure the security and operability of their IoT devices while maintaining the integrity of their network defenses? Effectively managing IoT devices behind a firewall is no longer a luxury, but a necessity in today's hyper-connected world. This requires a strategic blend of tools, techniques, and best practices to navigate the complexities of securing a rapidly expanding network of interconnected devices.
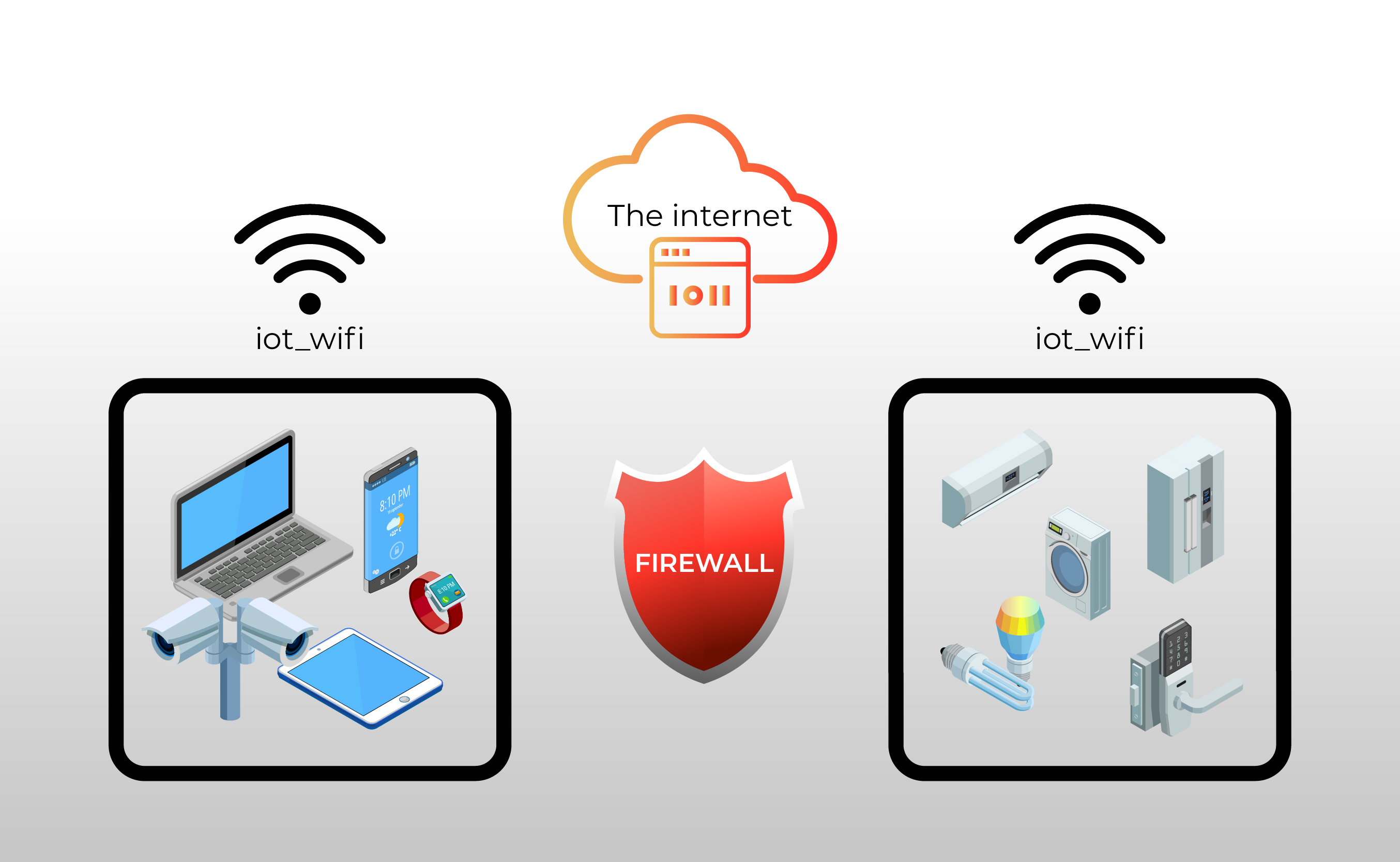
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to transportation and home automation. This interconnected web of devices, embedded with sensors and software, collects and exchanges data, enabling unprecedented levels of automation, efficiency, and insight. However, this interconnectedness presents significant security challenges, particularly when these devices operate behind a firewall. Firewalls, designed to protect internal networks from unauthorized access, can inadvertently hinder the functionality and management of IoT devices. This article delves into the intricacies of managing IoT devices behind a firewall, exploring the tools, strategies, and best practices required to achieve both robust security and seamless operation.
| Topic | Information |
|---|---|
| Definition of IoT | A network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity which enables these objects to connect and exchange data. |
| Firewall | A network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. |
| Key Challenges | Security vulnerabilities, network complexity, device heterogeneity, scalability, and lack of standardization. |
| Tools and Technologies | VPN, SSH, Port Forwarding, Network Segmentation, Cisco IoT Field Network Director, Remote.it, SocketXP. |
| Best Practices | Implement strong authentication, encrypt data in transit and at rest, regularly update firmware, segment networks, monitor network traffic, and develop an incident response plan. |
| Further Reading | Cisco IoT Field Network Director |
One fundamental approach to managing IoT devices behind a firewall involves network segmentation. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, organizations can limit the impact of a security breach. If one segment is compromised, the others remain protected, preventing widespread damage. This strategy enhances security by containing threats and reducing the attack surface.
Several tools and technologies facilitate secure IoT device management. Cisco IoT Field Network Director, for example, provides centralized control and automation, simplifying device management and enhancing security. Remote.it offers a powerful solution enabling users to connect to devices behind firewalls and NAT, ensuring seamless connectivity without compromising security. SocketXP, another cloud-based solution, provides secure remote access and device management, allowing SSH access to remotely located IoT devices such as Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and Nvidia Jetson. These tools empower administrators to effectively manage and monitor devices, regardless of their location.
Port forwarding, VPNs, and SSH are essential techniques for securely accessing and managing IoT devices behind firewalls. Port forwarding allows specific ports on the firewall to be opened, directing traffic to the internal IP address of the IoT device. VPNs create secure, encrypted connections between devices and the network, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. SSH provides a secure shell for managing and configuring devices remotely. Utilizing these techniques effectively strengthens security and ensures seamless device operation.
Implementing robust security measures is paramount for protecting IoT devices and the networks they operate on. Strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, should be employed to verify the identity of users and devices attempting to access the network. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, protects sensitive information from unauthorized access. Regular firmware updates patch security vulnerabilities and ensure devices operate with the latest security features. These practices are crucial for mitigating risks and maintaining a secure IoT environment.
Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity is critical for detecting and responding to security threats. Firewalls play a vital role in capturing and logging all traffic, providing valuable insights into network activity. This data enables security systems to correlate information from multiple firewalls, identify anomalies, and trigger alerts. Real-time monitoring allows for rapid response to security incidents, minimizing potential damage.
The challenges of managing IoT devices behind a firewall are numerous. The sheer number of devices, often heterogeneous in nature, presents significant management complexity. Ensuring the security of these devices, each with its own vulnerabilities, requires a multifaceted approach. Scalability is another key concern, as the number of connected devices continues to grow exponentially. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic blend of tools, technologies, and best practices.
Remote management of IoT devices is not merely a matter of convenience; its about maintaining control, ensuring optimal functionality, and addressing issues proactively. Without proper access, troubleshooting becomes a nightmare, and downtime can lead to significant losses. Remote management tools empower administrators to diagnose problems, apply updates, and configure devices remotely, minimizing disruptions and ensuring business continuity.
In conclusion, managing IoT devices behind a firewall requires a comprehensive and strategic approach. By leveraging the right tools, implementing robust security measures, and adopting best practices, organizations can harness the full potential of the IoT while mitigating the inherent security risks. This proactive approach ensures the seamless operation, security, and scalability of IoT deployments, enabling businesses to thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.