Ruptured Spleen: Signs, Symptoms, & Emergency Care | [Keyword]
Is a sudden, sharp pain in your abdomen a sign of something serious? A ruptured spleen, a medical emergency, demands immediate attention and can be life-threatening.
Understanding the intricacies of this condition is crucial, encompassing its causes, recognizable symptoms, diagnostic processes, and available treatment options. This article aims to provide comprehensive insights into this critical medical issue, ensuring you have the knowledge necessary to identify potential problems and seek timely medical intervention.
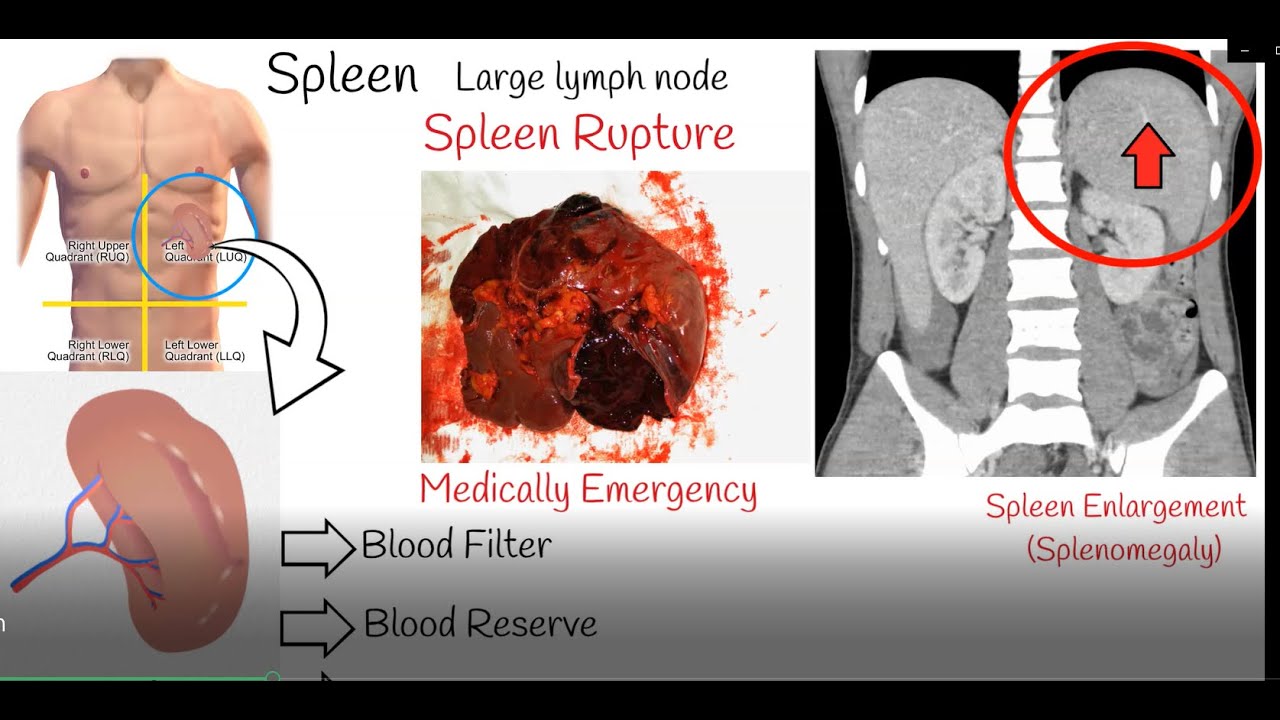
The spleen, often overlooked, is a vital organ located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, nestled behind the ribs. Its primary functions include filtering blood, removing old or damaged blood cells, and housing white blood cells that contribute to the body's immune defense. However, the spleen is susceptible to injury, and when it ruptures, the consequences can be dire.
A ruptured spleen, essentially, is a tear in the spleen's capsule, leading to internal bleeding. This can occur due to various factors, most commonly blunt force trauma to the abdomen. This trauma can stem from a car accident, a sports injury, or even a forceful blow. Less frequently, the spleen may rupture spontaneously, often due to underlying medical conditions that weaken the organ, such as certain infections, enlarged spleens (splenomegaly), or cancerous tumors.
Recognizing the symptoms of a ruptured spleen is paramount for prompt medical attention. These symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the rupture and the extent of internal bleeding. However, certain signs are commonly associated with this condition:
- Pain in the Upper Left Abdomen: This is the most prevalent symptom, often described as sharp, intense, and localized to the area of the spleen.
- Tenderness upon Palpation: Touching the upper left abdomen can elicit significant pain.
- Referred Pain: Pain may radiate to the left shoulder, a phenomenon known as Kehr's sign, caused by blood irritating the diaphragm.
- Lightheadedness and Dizziness: These symptoms may result from blood loss and a decrease in blood pressure.
- Blurred Vision: Diminished blood flow can also affect vision.
- Confusion: Severe blood loss can affect brain function.
- Signs of Shock: In cases of significant blood loss, individuals may exhibit signs of shock, including rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, and clammy skin.
If you experience these symptoms after a potential abdominal injury or if you have any concerns about your health, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial. A ruptured spleen is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing a ruptured spleen typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and blood tests. The physician will begin by assessing your symptoms and conducting a physical examination, focusing on the abdomen. Imaging tests, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen, are often utilized to visualize the spleen and identify any evidence of rupture or internal bleeding. A CT scan can provide detailed images of the spleen, allowing for the detection of tears or other structural damage. Blood tests can help assess blood loss, check for internal bleeding, and evaluate overall health status.
Treatment for a ruptured spleen depends on the severity of the injury. In some cases, if the rupture is minor and bleeding is minimal, the condition may be managed conservatively. This may involve close monitoring in a hospital setting, rest, and avoiding strenuous activities to allow the spleen to heal. However, if the rupture is severe, or if significant bleeding is present, surgery is often required. Surgery may involve:
- Splenectomy: The complete removal of the spleen. This is the most common surgical treatment for a ruptured spleen, especially if the injury is severe or the spleen is severely damaged.
- Splenic Repair: In some cases, the surgeon may be able to repair the ruptured spleen using stitches or other techniques. This approach is more common in less severe cases and aims to preserve the spleen's function.
After surgery, patients are closely monitored during their recovery phase. Individuals who have undergone a splenectomy are at an increased risk of certain infections because of the spleen's role in the immune system. Therefore, they typically receive vaccinations to protect against specific infections. They may also need to take antibiotics preventively to lower the risk of infection.
Complications of a ruptured spleen can range from mild to severe. One of the primary risks is significant blood loss, which can lead to hemorrhagic shock and potentially be life-threatening. Infections are another serious concern, especially for those who have had their spleen removed. The spleen plays a key role in the immune system, so its absence makes individuals more susceptible to infections like pneumococcal pneumonia, Haemophilus influenzae, and meningococcal infections. Other potential complications include:
- Delayed Bleeding: Bleeding may continue even after the initial injury, potentially leading to further complications.
- Abdominal Compartment Syndrome: Swelling and bleeding can cause increased pressure in the abdomen, potentially restricting blood flow to organs.
Preventing a ruptured spleen involves avoiding traumatic injuries and managing underlying conditions that may increase the risk of spleen rupture. These measures include:
- Wearing Seatbelts: Always use seatbelts in vehicles to reduce the risk of abdominal injury in car accidents.
- Using Protective Gear: Wearing appropriate protective gear during sports and other activities that involve a risk of abdominal injury.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Addressing any underlying conditions that may weaken the spleen, such as infections, and ensuring prompt medical attention.
Understanding the nuances of a ruptured spleen requires a broader perspective that considers causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. This knowledge enables informed decisions and proactive approaches to safeguarding health.
In the context of sports, the spleen is vulnerable to injury, making athletes in contact sports, such as football, rugby, and martial arts, particularly susceptible to splenic rupture. A direct blow to the abdomen or a sudden deceleration can result in a splenic injury. The severity of the injury can vary from minor contusions (bruising) to complete rupture. The role of the physical therapist is to recognize signs and symptoms of a potential splenic rupture, which is often critical. Immediate medical attention is imperative, and treatment focuses on stabilizing the patient and preventing further blood loss. Return-to-play guidelines after splenic injury will depend on the extent of the injury and the type of treatment.
In the realm of veterinary medicine, a ruptured spleen in dogs presents a serious health issue, demanding immediate veterinary intervention. The spleen in dogs, like humans, is a vital organ that filters blood and stores red blood cells. Splenic ruptures can occur due to trauma, such as being hit by a car, or they can be caused by tumors, specifically hemangiosarcoma, a type of cancer that commonly affects the spleen in dogs. The symptoms of spleen rupture in dogs can vary but often include:
- Lethargy
- Weakness
- Abdominal distension (bloating)
- Pale gums
- Loss of appetite
Veterinarians diagnose a ruptured spleen in dogs through physical examination, imaging (such as ultrasound or X-rays), and blood tests. Treatment options commonly involve surgery to remove the spleen, called a splenectomy. The long-term prognosis for dogs depends on the underlying cause and the success of the surgery. Early detection and intervention significantly improve the chances of survival and recovery.
The physical therapist also plays an essential role in the comprehensive care of individuals recovering from splenic injuries. They must possess a keen ability to recognize the signs and symptoms of splenic rupture. The physical therapist's role includes assessing the patient's physical capabilities, designing a rehabilitation program to restore strength and flexibility, and educating the patient about the importance of cautious movements and recognizing potential complications. As the individual progresses through rehabilitation, the physical therapist also gradually guides them to regain functional abilities and a safe return to activities, and they carefully monitor for any signs of recurrence or complications.
Research and advancements in medical knowledge have contributed to a more thorough understanding of splenic injuries. Current trends encompass:
- Enhanced Imaging Techniques: The implementation of high-resolution imaging techniques, such as advanced CT scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), enables more precise and detailed assessment of splenic injuries, leading to more accurate diagnosis and management.
- Surgical Approaches: Progress in surgical techniques has led to more minimally invasive approaches, such as laparoscopic splenectomy, reducing post-operative recovery time and complications.
- Medical Management: Improved critical care protocols and medications can contribute to the stabilization of patients experiencing internal bleeding.
The spleen's vulnerability to injury, the importance of prompt recognition of symptoms, the array of diagnostic tests, and the treatment choices are all vital components of the clinical perspective for this dangerous medical condition. It highlights the need for a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to managing this critical medical emergency.