GMT Time Explained: Current Time, Zones & Conversions
Do you ever find yourself puzzling over time zones, those invisible lines that dictate the rhythm of our global interactions? Understanding Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) isn't just about knowing the current time; it's about grasping a foundational concept that underpins how we coordinate activities across the world, from scheduling international calls to tracking the movements of celestial bodies.
Greenwich Mean Time, often abbreviated as GMT, is a term that resonates with anyone who has navigated the complexities of international communication or travel. It's the local mean time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, the point from which all other time zones are referenced. This system, born from a need for standardized timekeeping, has evolved into a crucial element of our interconnected world. The concept of GMT has its roots in the need for maritime navigation. Before the advent of precise timekeeping, sailors struggled to determine their longitude, crucial for plotting their course. The establishment of the Royal Observatory in Greenwich in 1675 marked a pivotal moment. This institution, with its dedication to astronomical observation, was instrumental in developing the tools and techniques necessary for accurate timekeeping, including the calculation of GMT.
At various points in history, GMT has been calculated in different ways. Initially, it was reckoned from noon, but now it is counted from midnight, making it easier to align with the 24-hour clock system widely used today. The evolution of GMT reflects the broader advancements in scientific understanding and technological capabilities. This is precisely why context is essential when referencing a time. You will find the exact current GMT time, along with the various locations that utilize GMT as their standard time, providing a universal reference point for global timekeeping.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) |
| Definition | The local mean time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, used as a reference for time zones. |
| Origin | Royal Observatory, Greenwich, London, established in 1675. |
| Location | The zero-degree longitude line (Prime Meridian) passes through Greenwich. |
| Also known as | UTC 0 and corresponds to Western European Time (in some countries). |
| Purpose | To serve as a global time standard, facilitating navigation and international coordination. |
| Relationship with UTC | GMT has no offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). |
| Time Calculation | Calculated from midnight. It was once calculated from noon. |
| Importance | Crucial for coordinating international events, travel, and communications. |
| Areas of application | Navigation, astronomy, aviation, and global business operations |
| Time Zone Offset | UTC+0 |
| Observed In | United Kingdom, Ireland, Iceland, Portugal, Canary Islands, and parts of West Africa. |
| Historical Context | Originated from the need for precise maritime navigation. |
| Current Status | Still a fundamental reference point for time zones. |
| Conversion | Easily convertible to other time zones. |
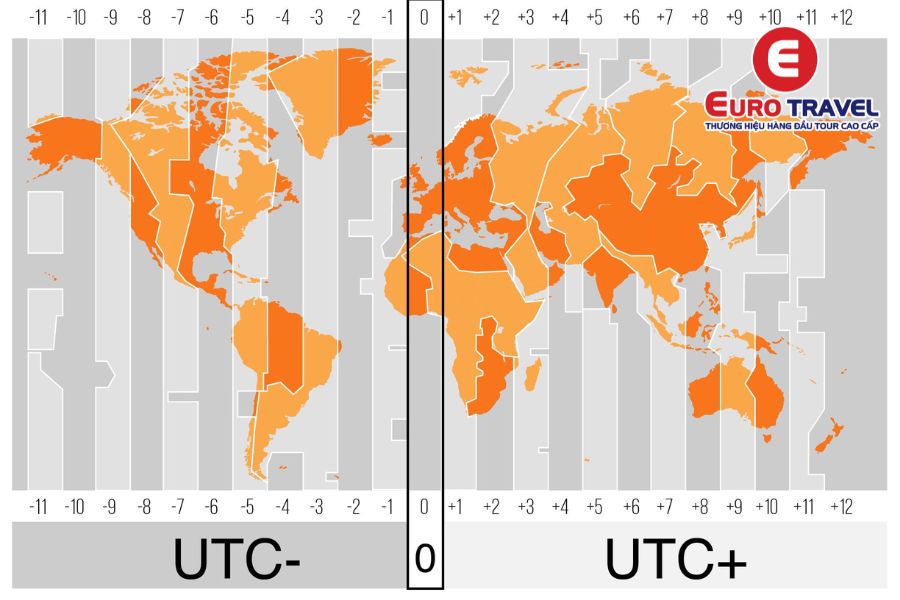
GMT's influence extends far beyond simply telling time. It serves as a foundation for understanding the complex network of time zones that span the globe. It is a central reference point, UTC 0, from which all other time zones are calculated. Each time zone is defined by its offset from GMT, either adding or subtracting hours, depending on its location relative to the Prime Meridian. For example, Eastern Standard Time (EST) is UTC -5, meaning it is five hours behind GMT.
The widespread adoption of GMT was driven by necessity. As international travel and communication increased, the need for a common time standard became critical. Different regions and countries had their own local times, which made coordinating activities across borders extremely challenging. GMT provided a universal reference that simplified scheduling and ensured that everyone was on the same page, regardless of their geographic location.
You will find various tools and resources that use GMT for conversions. Whether youre planning a trip, scheduling a conference call, or simply trying to understand the time difference between two locations, GMT serves as a crucial tool. These converters allow users to input a time in one time zone and instantly see the corresponding time in others. This feature is beneficial for various tasks such as converting time between multiple locations, checking time zones, and planning events. You can convert time between locations, check timezone time, city time, and plan travel time by using these resources, that will surely help you.
The concept of GMT isn't static; its an integral part of a constantly evolving global system. GMT and the other time zones also accommodate for daylight saving time (DST). This seasonal adjustment, where clocks are moved forward by an hour during the warmer months, is implemented to make better use of daylight. GMT's role is vital in understanding how these adjustments impact timekeeping around the world. GMT, however, is not always affected by DST, it serves as a constant reference.
While GMT is a widely understood term, it's essential to recognize its relationship with Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. GMT is, in essence, a time zone, while UTC is the scientific standard. GMT does not have an offset from UTC, they are essentially the same for the time being. UTC is based on atomic clocks, which are incredibly precise, whereas GMT, as a mean solar time, can be subject to slight variations due to the Earth's orbit.
The concept of GMT extends into various fields, each with its own specific needs and requirements. In aviation, for example, all flight plans and schedules are coordinated using UTC. Pilots and air traffic controllers rely on this universal time to ensure the safe and efficient operation of flights across the globe. Similarly, in the world of finance, where milliseconds can make a difference, a standardized time system is critical for the accurate recording of transactions. Moreover, astronomers and other scientists use GMT to record astronomical events and collect scientific data, as they need a universally agreed-upon time to avoid any discrepancies in their findings.
The implementation of GMT has had a profound impact on how we conduct business, organize events, and travel. It has enabled global collaboration and communication. With GMT as a central point, individuals and organizations are able to coordinate their schedules, organize international events, and conduct business across various time zones with ease.
The history of timekeeping is a fascinating one, and GMT's journey is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of accuracy. From the earliest sundials to the modern atomic clocks, the evolution of timekeeping reflects our ability to innovate and adapt. The Royal Observatory in Greenwich, a pioneer in timekeeping, played a pivotal role in this evolution. The instruments and techniques developed there were fundamental to establishing GMT as a standard. The Prime Meridian, the line of zero longitude that passes through Greenwich, is a direct result of these efforts. It divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres, serving as a reference point for all longitude measurements.
GMT and the concept of time zones are not just abstract ideas; they are integral to our everyday lives. From the moment you wake up and check the time on your phone to the moment you plan a vacation or attend an international meeting, GMT plays a role. Understanding GMT allows us to navigate the complexities of a globalized world, allowing us to stay connected and coordinated with people all over the planet. It's a bridge that connects cultures and facilitates collaboration.
The use of GMT is also deeply entrenched in various technological systems. GPS, the satellite-based navigation system, relies on UTC. This means that every device using GPS, from smartphones to car navigation systems, synchronizes its time with UTC. Furthermore, servers that host websites and applications use GMT to record the time of events and transactions. The prevalence of GMT in technology highlights its importance in the digital age, shaping how we interact with technology and each other.
Moreover, the role of GMT is set to evolve with the continuous advancements in technology and changes in global dynamics. As technology advances, the accuracy and synchronization of timekeeping systems will continue to improve. GMT serves as a foundation for these developments. The need for accurate and reliable time will only increase, making GMT even more important in the future.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the local mean time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London. It is a standard that has played an important role in global coordination, facilitating navigation, scheduling, and scientific research. GMT has no offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). GMT's significance extends to various fields, including aviation, finance, and astronomy, where accurate timekeeping is crucial. Understanding GMT enhances our ability to interact in a world where activities are carried out across multiple time zones.
The conversion of time between multiple locations, timezone checks, and flight arrival time calculations, all depend on GMT as a cornerstone. As we move forward in the digital age, GMT's role will evolve. It will be an essential standard for global communication and cooperation.
The essence of GMT is reflected in the expression of various time zone offsets from UTC. You can see time zone differences in relation to GMT by using applications to plan and schedule events or meetings. GMT's role continues to be essential in facilitating global synchronization.